The James Webb Space Telescope or JWST is the most potent telescope ever inaugurated into space. This telescope was launched by NASA on an Ariane 5 rocket from the Spaceport of European in South America on December 25, 2021, to conduct infrared astronomy. The advanced infrared sensitivity and resolution of this telescope will help to view the old and distant astronomical objects. NASA is expecting that the JWST will conduct a wide range of investigations within the fields of cosmology and astronomy including a detailed description of potentially habitable exoplanets, and the observations of how the first stars and galaxies formed. Recently, on 1st June, NASA stated that the first images from the Webb Space Telescope will be released on July 12, 2022.
The Development of the JWST:
In collaboration with the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and European Space Agency (ESA), NASA (the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration) conducted the development of the JWST. The main contractor of this project was Northrop Grumman. The NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Maryland oversaw the entire development process while the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore is responsible for operating the JWST. To honor the former administrator of NASA, James E. Webb, this telescope was named after his name.
Features:
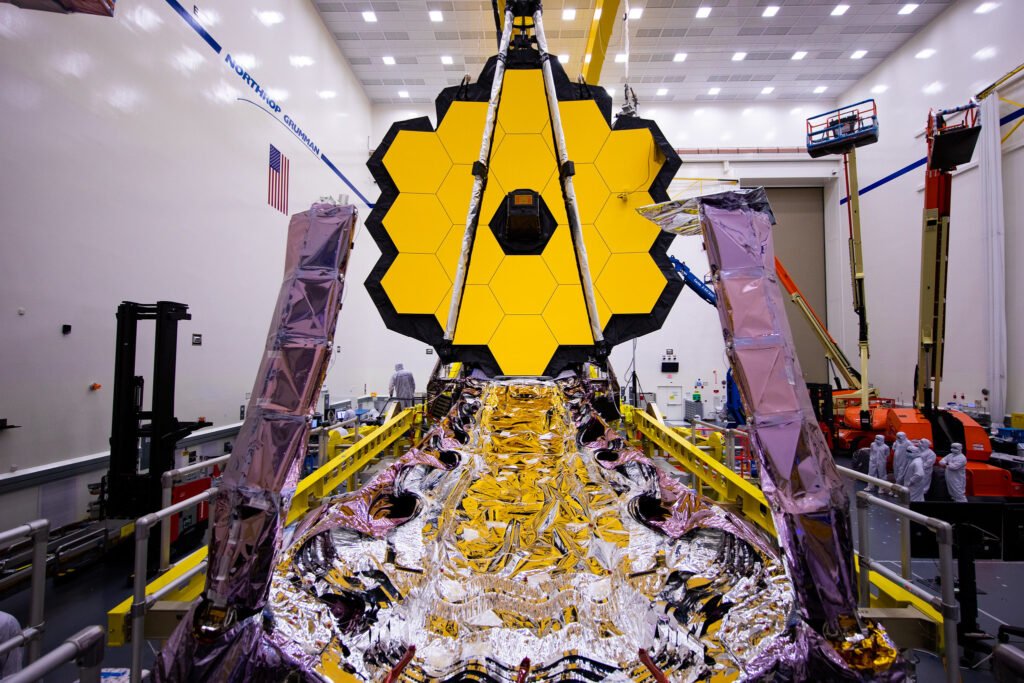

The mass of the JWST is about half of the mass of the Hubble Space Telescope. The diameter of this telescope is 6.5 meters, and it involves18 separate gold-coated beryllium hexagonal mirrors. The collecting area (25.4 square meters) of the mirror is more than six times larger than the collecting area (4.0 square meters) of Hubble’s mirror. To improve infrared reflectivity and durability, the mirror consists of a gold coating. Even though the design of the JWST focuses on near-infrared astronomy, it can also perceive the mid-infrared region, and red and orange visible light.
JWST Science:
The purpose of the JWST is to investigate each phase of cosmic history starting from the Big Bang and the glow of the first luminous to the formation of stars, galaxies, and planets to the progress of our solar system. The four main science goals of the James Webb Space Telescope are-
The End of the Dark Ages:
With the infrared vision, JWST will investigate the appearance of the first light and look back to over 13.5 billion years to understand how the early universe including the first stars and galaxies formed out of the darkness.
Assembly of Galaxies:
With the help of the exceptional infrared sensitivity of JWST, astronomers will be able to make a comparison between eh earliest galaxies and today’s grand ellipticals and spirals. Therefore, the astronomers will be able to recognize how the assembly of galaxies occurred over billions of years.
The Creation of Protoplanetary Systems and Stars:
JWST will be able to perceive light through immense clouds of dust and therefore, it will give information regarding the creation of stars and planetary systems.
Planetary Systems and the Roots of Life:
JWST will study the atmosphere of extrasolar planets and find life everywhere in the Universe. This telescope will also examine objects in our solar system.
Webb Recent News:
On 26th May, this year, NASA stated that the Webb is ready to investigate rocky worlds. They planned to investigate two hot exoplanets (known as super-Earths) for the first year. Within a few weeks, they will start studying geology from 50 light-years. The study of these two planets, such as lava-covered 55 Cancri e, and LHS 3844 b can give us some important information. Later, on 1st June, NASA declared that JWST has been going through the preparation phase for a six-month period and it has built the spectroscopic data and the first full-color images that NASA will release on July 12, this year. Then the scientific observations of JWST will start and the telescope will continue to investigate major science themes.